Appearance
Spring Boot 基础
创建一个入门程序
- 新建一个模块
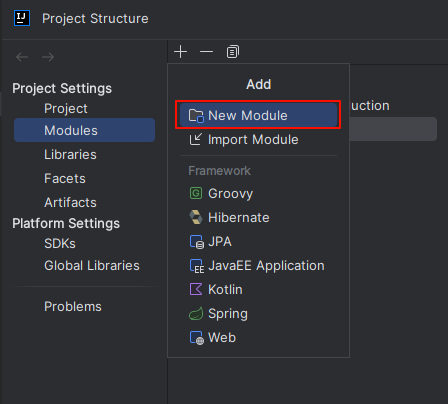
- 选择 spring 启动器
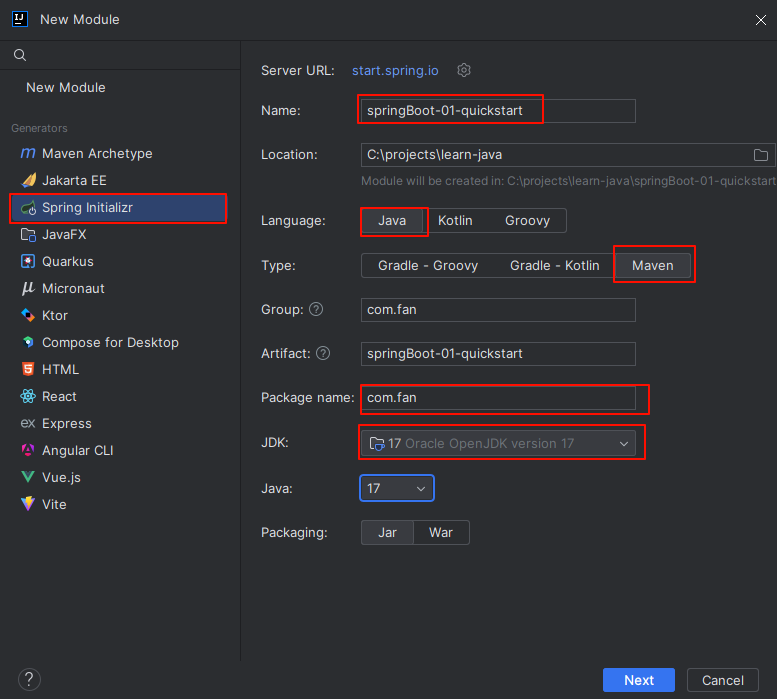
- 选择 spring boot 版本,如果是 web 项目,可以勾选 spring web
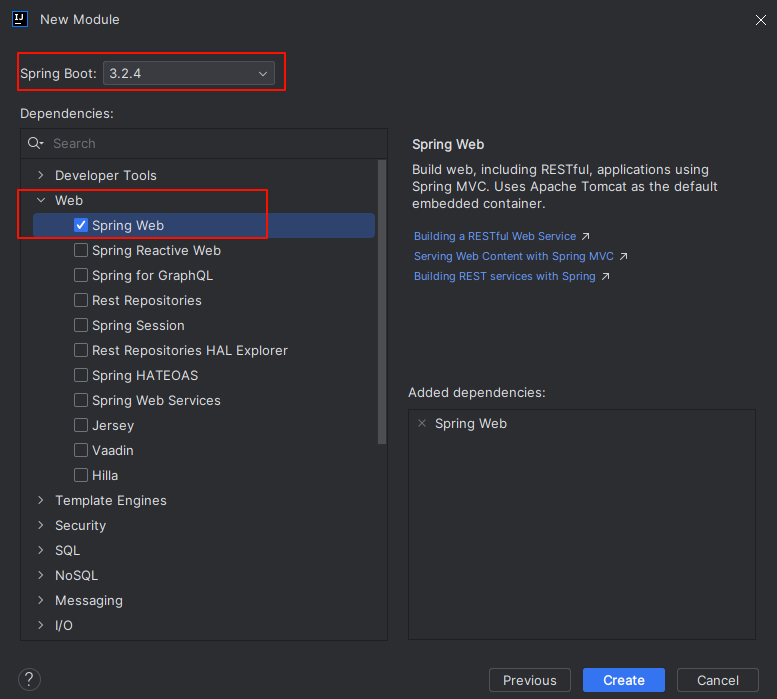
- 项目结构,可以把除了 src 和 pom.xml 的其他文件都删掉,留着也没事,暂时用不到
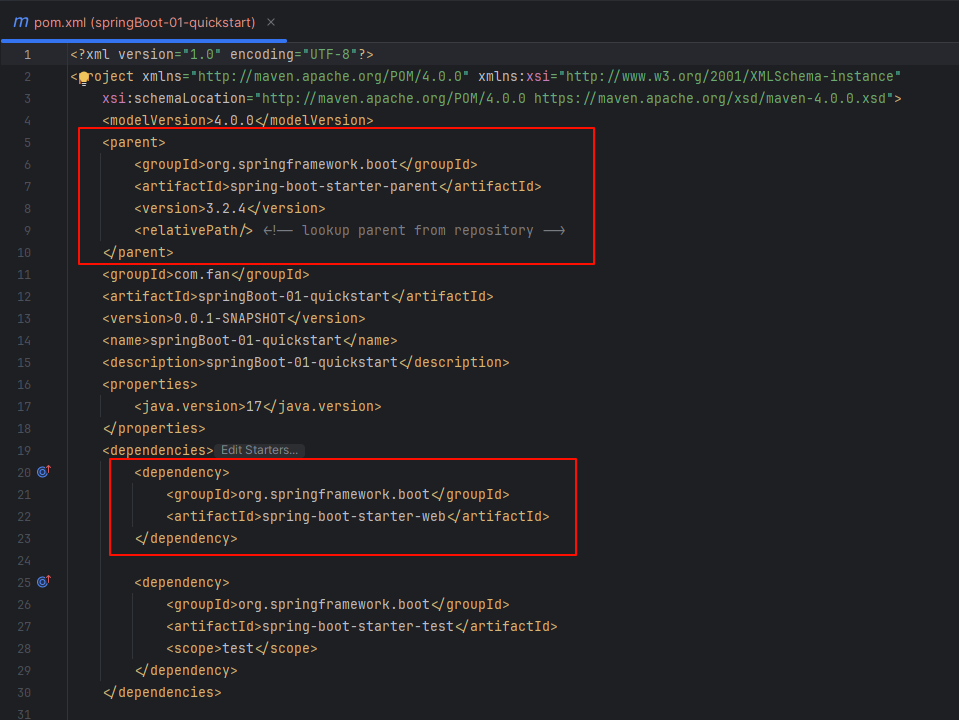
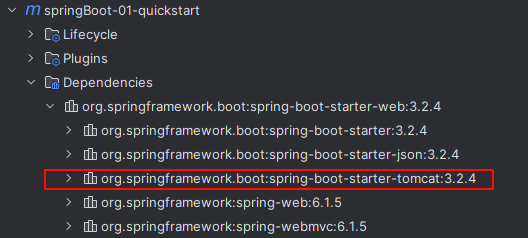
- 查看 pom 文件,我们会发现它继承了
spring-boot-starter-parent,使用了 web 依赖,web依赖里面有使用到 tomcat
parent:所有SpringBoot项目要继承的项目,定义了若干个坐标版本号(依赖管理,而非依赖),以达到减少依赖冲突的目的
实际开发中
- 使用任意坐标时,仅书写GAV中的G和A,V由SpringBoot提供
- 如发生坐标错误,再指定version(要小心版本冲突)
- 试着写一个 controller,然后启动 Application
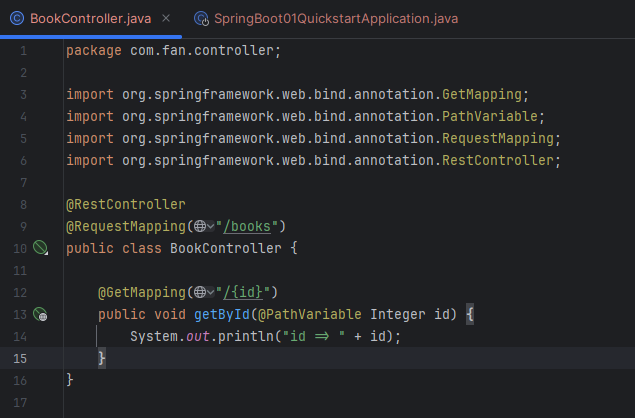
java
package com.fan.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/books")
public class BookController {
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public void getById(@PathVariable Integer id) {
System.out.println("id => " + id);
}
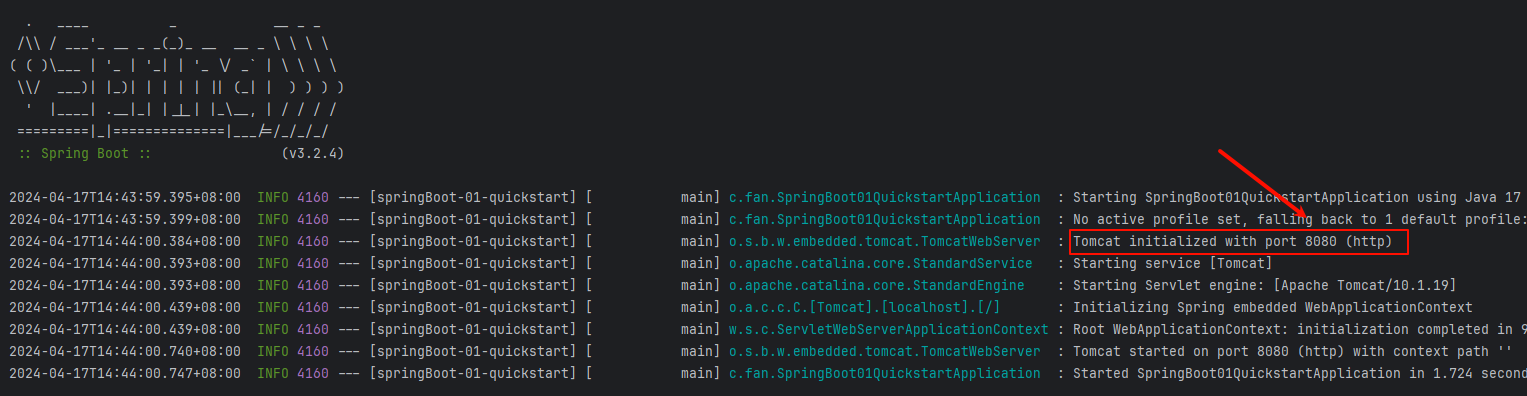
}可以发现,成功启动在了 8080 端口
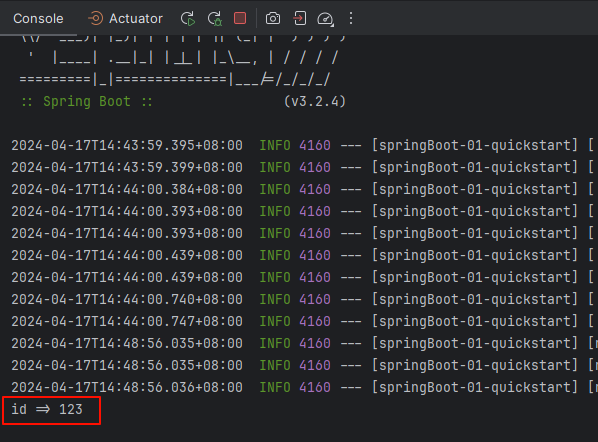
使用 postman 请求 http://localhost:8080/books/123,控制台成功打印了我们请求的 id
SpringBoot 项目快速启动
SpringBoot 提供了一个很有意思的功能,它 pom 里面还依赖了一个 maven plugin 的插件。它可以通过 maven 进行打包,打包成一个 jar 包,然后可以通过命令行的方式启动它。它的应用场景是啥呢,如果前端需要在他本地起一个后端服务,就不用下那么多复杂的东西,直接把打包好的 jar 文件发给他,他就能在本地调试前端代码了。
- 双击 maven 的 package 进行打包
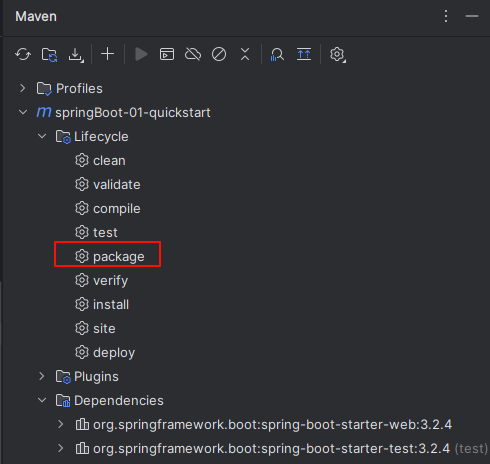
- 打包完成后,可以在 target 文件夹下看到我们打好的 jar 包
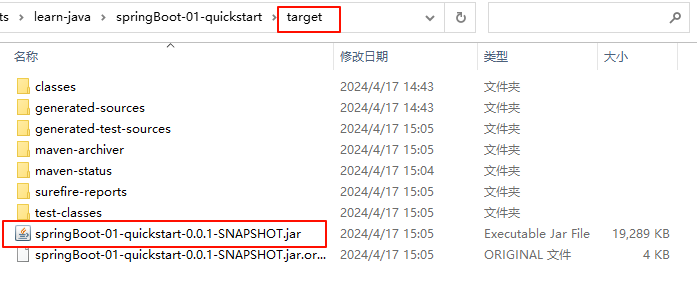
- 在当前目录下打开命令行,执行
java -jar 包名就可以运行 spring boot 程序了
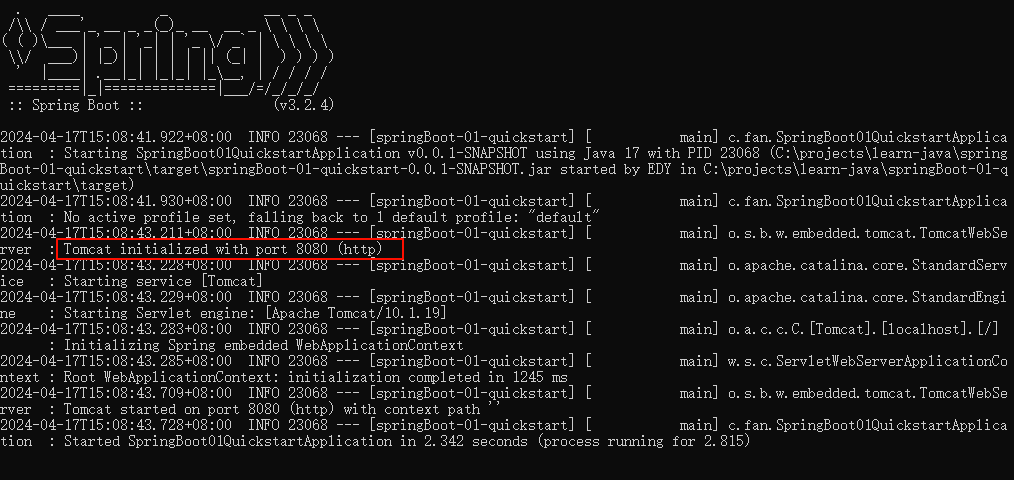
注意:jar支持命令行启动需要依赖maven插件支持,请确认打包时是否具有SpringBoot对应的maven插件
xml
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>修改默认扫描包
springboot 会默认扫描一些包,但是如何我们在这些包外面新建文件编写代码,他就扫描不到,我们可以在启动类中的 @SpringBootApplication 注解中配置 scanBasePackages 指定我们需要扫描哪些包的路径,它可以是多个也可以是单个。
java
@SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages = {"com.fan"})
public class SpringBootApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootApplication.class, args);
}
}切换 tomcat 为 jetty(辅助功能)
在上面已经知道了,starter-web 中自带 tomcat,我们点进去看下
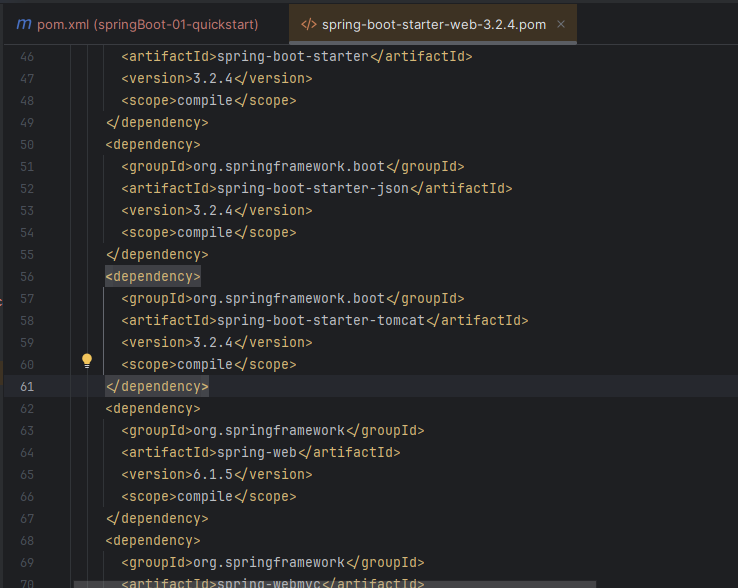
配置排除依赖,排除掉 tomcat
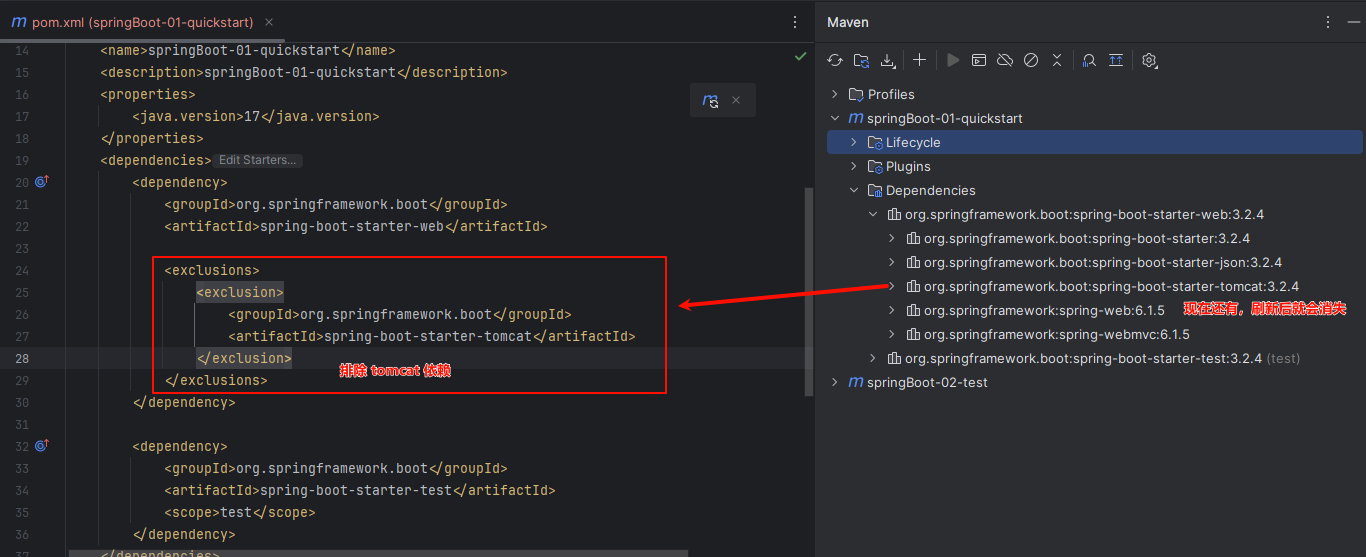
xml
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>刷新后,依赖就排除了
添加 jetty 依赖
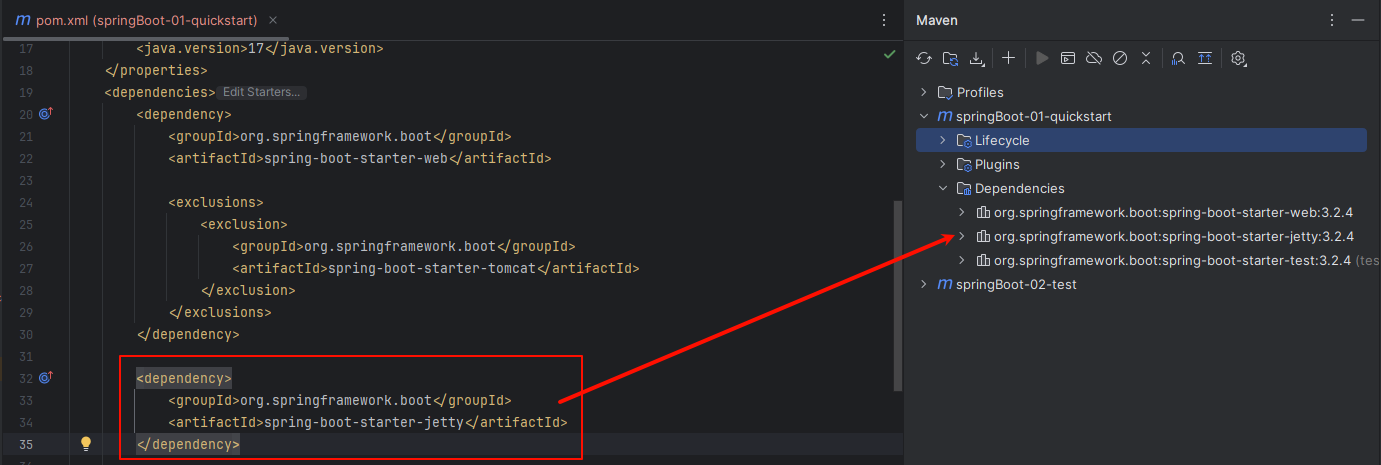
xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jetty</artifactId>
</dependency>启动 Application 类,一样是启动成功的,在 8080 端口,使用的是 jetty web服务器
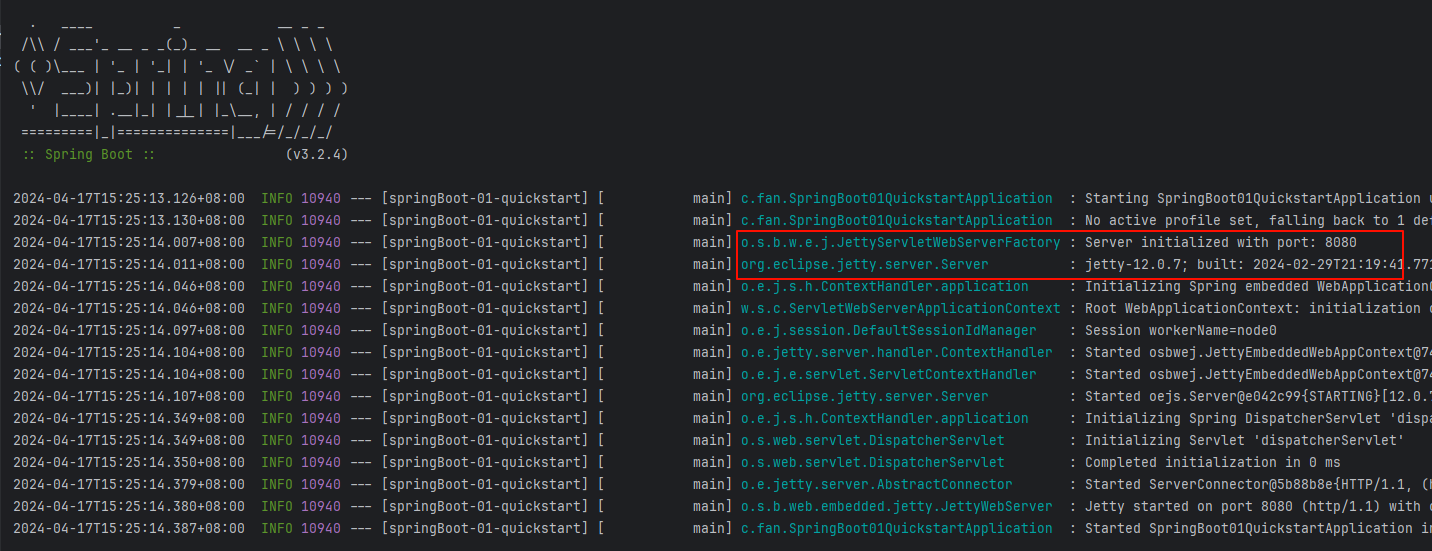
jetty 对比 tomcat web服务器相对来说是轻量级的,很多东西都需要自己配,tomcat 是配置好的,在项目中 tomcat 用的比较多
配置文件
SpringBoot提供了多种属性配置方式
- application.properties
properties
server.port=81- application.yml
yaml
server:
port: 82- application.yaml
yaml
server:
port: 83SpringBoot 配置文件加载顺序:(yml 常用一些)
application.properties > application.yml > application.yaml
注意事项:
- SpringBoot核心配置文件名为application
- SpringBoot内置属性过多,且所有属性集中在一起修改,在使用时,通过提示键+关键字修改属性
读取配置文件
application.yml 配置如下
yml
learn: java
server:
port: 82
age: 18
subject:
- java
- 前端
- 全栈有三种方式读取配置文件:
- 使用
@Value注解的方式,读取单个数据,@Value("${属性名.(多层级)[下标]}")
java
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/books")
public class BookController {
// @Value 的方式
@Value("${learn}")
private String learnName;
@Value("${server.port}")
private String port;
@Value("${server.subject[0]}")
private String subject_00;
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public void getById(@PathVariable Integer id) {
System.out.println("id => " + id);
System.out.println("--------------------");
System.out.println(learnName);
System.out.println(port);
System.out.println(subject_00);
}
}- 使用 Environment 对象,全部数据都封装到了改对象,可以使用
getProperty(“属性名”)来读取
java
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/books")
public class BookController {
// Environment 的方式
@Autowired
private Environment env;
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public void getById(@PathVariable Integer id) {
System.out.println("id => " + id);
System.out.println("--------------------");
System.out.println(env.getProperty("learn"));
System.out.println(env.getProperty("server.port"));
System.out.println(env.getProperty("server.subject[1]"));
}
}- 自定义对象封装指定数据(常用)
创建一个实体类 com.fan.domain/Enterprise
java
package com.fan.domain;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Arrays;
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "server")
public class Enterprise {
private Integer port;
private Integer age;
private String[] subject;
public Integer getPort() {
return port;
}
public void setPort(Integer port) {
this.port = port;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String[] getSubject() {
return subject;
}
public void setSubject(String[] subject) {
this.subject = subject;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Enterprise{" +
"port='" + port + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", subject=" + Arrays.toString(subject) +
'}';
}
}java
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/books")
public class BookController {
// 自定义对象封装指定数据(常用)
@Autowired
private Enterprise server;
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public void getById(@PathVariable Integer id) {
System.out.println("id => " + id);
System.out.println("--------------------");
System.out.println(server.getPort());
System.out.println(server.getAge());
System.out.println(server.getSubject()[2]);
}
}总代码:
java
package com.fan.controller;
import com.fan.domain.Enterprise;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/books")
public class BookController {
// @Value 的方式
@Value("${learn}")
private String learnName;
@Value("${server.port}")
private String port;
@Value("${server.subject[0]}")
private String subject_00;
// Environment 的方式
@Autowired
private Environment env;
// 自定义对象封装指定数据(常用)
@Autowired
private Enterprise server;
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public void getById(@PathVariable Integer id) {
System.out.println("id => " + id);
System.out.println("--------------------");
System.out.println(learnName);
System.out.println(port);
System.out.println(subject_00);
System.out.println("--------------------");
System.out.println(env.getProperty("learn"));
System.out.println(env.getProperty("server.port"));
System.out.println(env.getProperty("server.subject[1]"));
System.out.println("--------------------");
System.out.println(server.getPort());
System.out.println(server.getAge());
System.out.println(server.getSubject()[2]);
}
}运行结果:

多环境配置
开发项目的时候,一般都有多个环境,比如生产环境(production)、开发环境(develop)、测试环境(test)。各个环境连接的数据库可能是不一样的,改来改去会很麻烦,可以先统一写好,再通过环境设置,就可以使用相同环境的配置了
yaml 文件多环境启动
比如我们切换不同环境的端口
yaml
# 配置当前使用的环境
spring:
profiles:
active: pro
---
# 生产环境
server:
port: 82
spring:
config:
activate:
on-profile: pro
---
# 开发环境
server:
port: 83
spring:
config:
activate:
on-profile: dev
---
# 测试环境
server:
port: 84
spring:
config:
activate:
on-profile: test
---properties 文件多环境启动
主要有四个文件
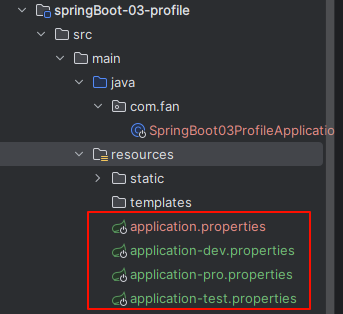
properties
#主启动配置文件 application.properties
spring.profiles.active=pro
#环境分类配置文件 application-pro.properties
server.port=85
#环境分类配置文件 application-dev.properties
server.port=86
#环境分类配置文件application-test.properties
server.port=87多环境启动命令格式
对 springboot 项目经 maven 打包,就可以使用命令来运行,命令也可以带参数,具体参数参考官网
bash
java –jar springboot.jar --spring.profiles.active=test
java –jar springboot.jar --server.port=88
java –jar springboot.jar --server.port=88 --spring.profiles.active=test配置优先加载顺序
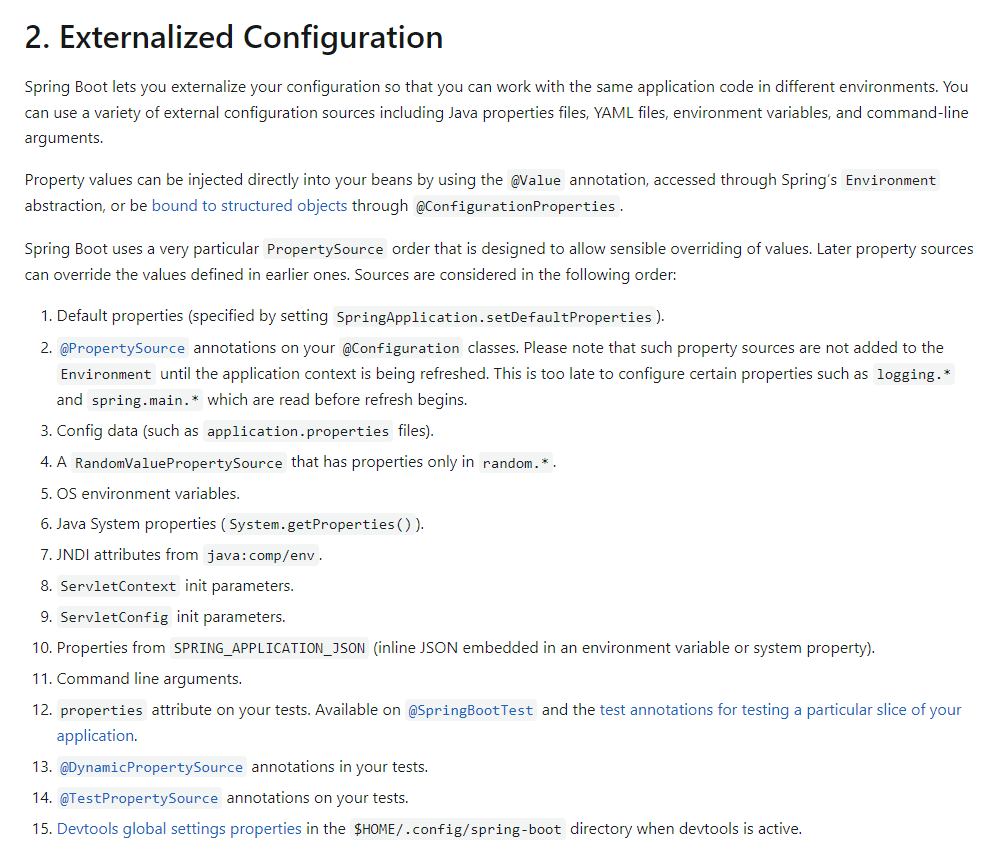
打包前可以先使用 maven 的 clean 进行清理,再进行打包。还将项目编码改成 utf-8,否则可能出现乱码
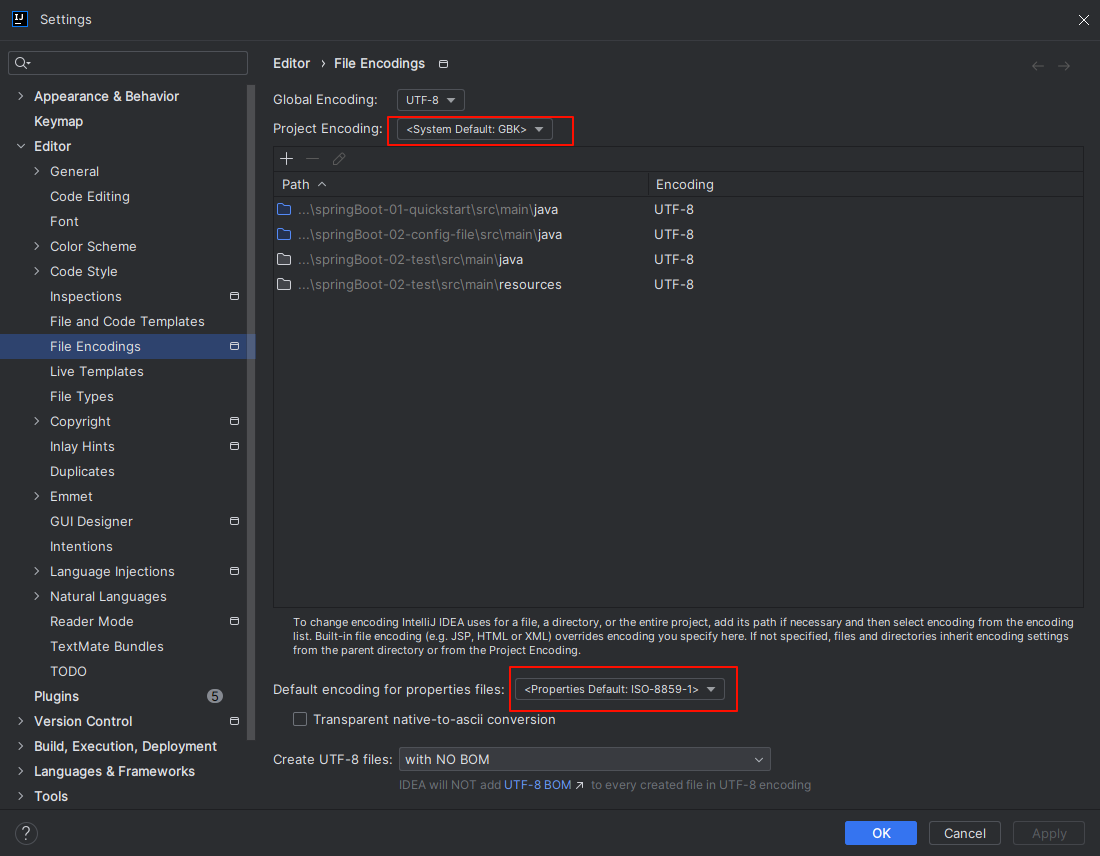
Maven 的多环境兼容
在 pom.xml 中加上配置
xml
<profiles>
<profile>
<id>pro</id>
<properties>
<profile.active>pro</profile.active>
</properties>
<activation>
<activeByDefault>true</activeByDefault>
</activation>
</profile>
<profile>
<id>dev</id>
<properties>
<profile.active>dev</profile.active>
</properties>
</profile>
<profile>
<id>test</id>
<properties>
<profile.active>test</profile.active>
</properties>
</profile>
</profiles>在 application.yml 中读取配置
yml
# 配置当前使用的环境
spring:
profiles:
active: ${profile.active}
---
# 生产环境
server:
port: 82
spring:
config:
activate:
on-profile: pro
---
# 开发环境
server:
port: 83
spring:
config:
activate:
on-profile: dev
---
# 测试环境
server:
port: 84
spring:
config:
activate:
on-profile: test
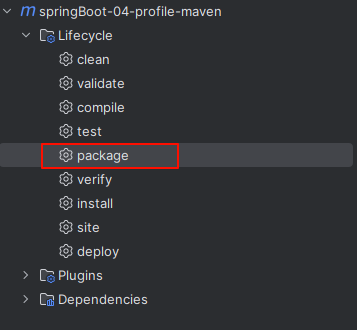
---使用 package 进行打包
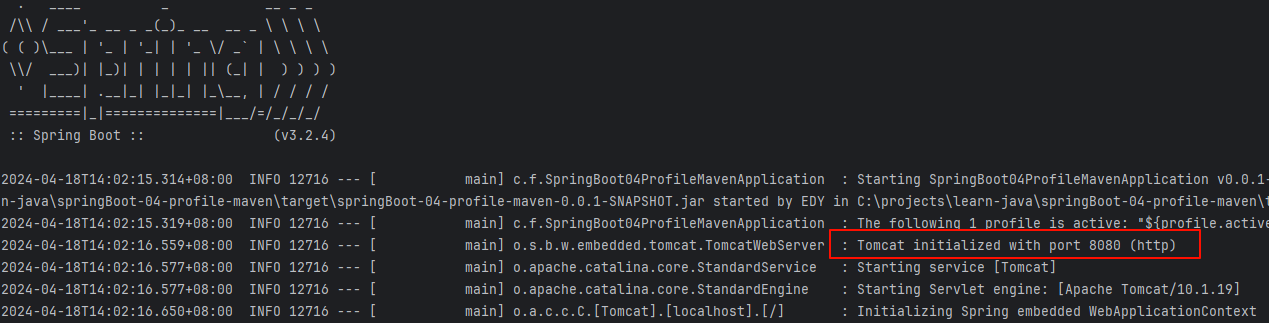
打包完在 target 目录下就有我们的 jar 包,我们运行它,会发现,它并没有在我们设置的端口上运行,而是在 8080 端口上运行了
用压缩软件打开打好的 jar 包,找到我们的 yml 配置文件
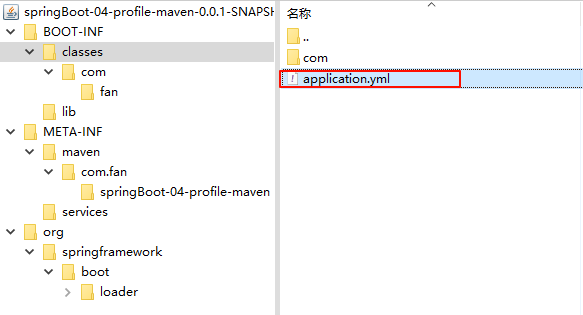
发现当前配置没配置上
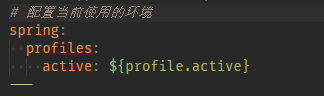
说明它没有解析,我们打包需要使用 maven-resources-plugin 插件,对 ${} 进行解析
xml
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-resources-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<encoding>utf-8</encoding>
<useDefaultDelimiters>true</useDefaultDelimiters>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
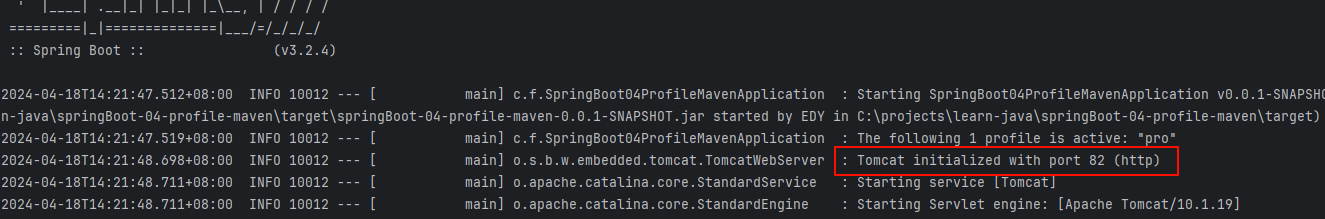
</build>使用命令运行,发现是我们设置的端口
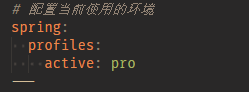
预览 jar 包里的配置文件,发现是成功解析了的
整合 JUnit
boot程序中已经给我们整合了 junit,只需要导入依赖 spring-boot-starter-test 即可
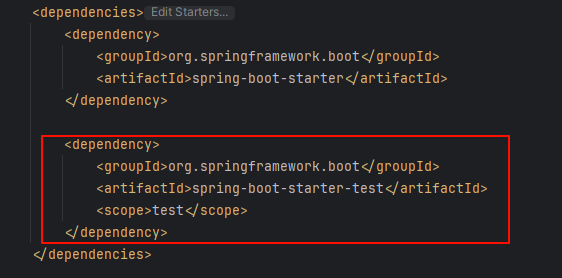
编写一个 service 来进行测试
java
// BookService
package com.fan.service;
public interface BookService {
public void save();
}java
// BookServiceImpl
package com.fan.service.impl;
import com.fan.service.BookService;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class BookServiceImpl implements BookService {
@Override
public void save() {
System.out.println("Hello Test");
}
}在测试类中编写代码
java
package com.fan;
import com.fan.service.BookService;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class SpringBoot05TestApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private BookService bookService;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
bookService.save();
}
}运行完成,控制台会打印 Hello Test
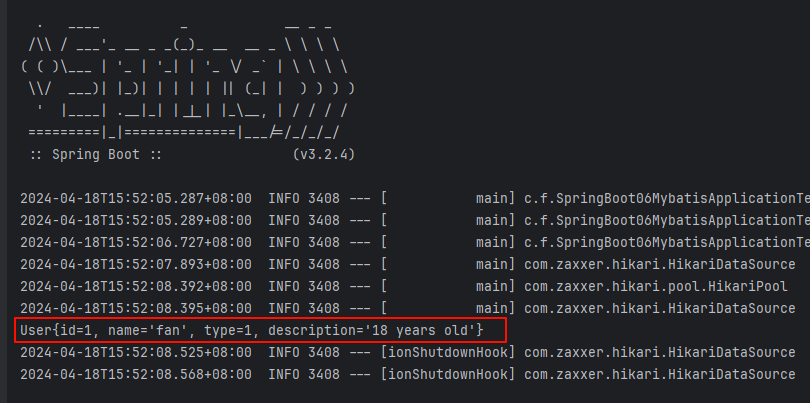
整合 MyBatis
创建项目时勾选我们所需要的依赖
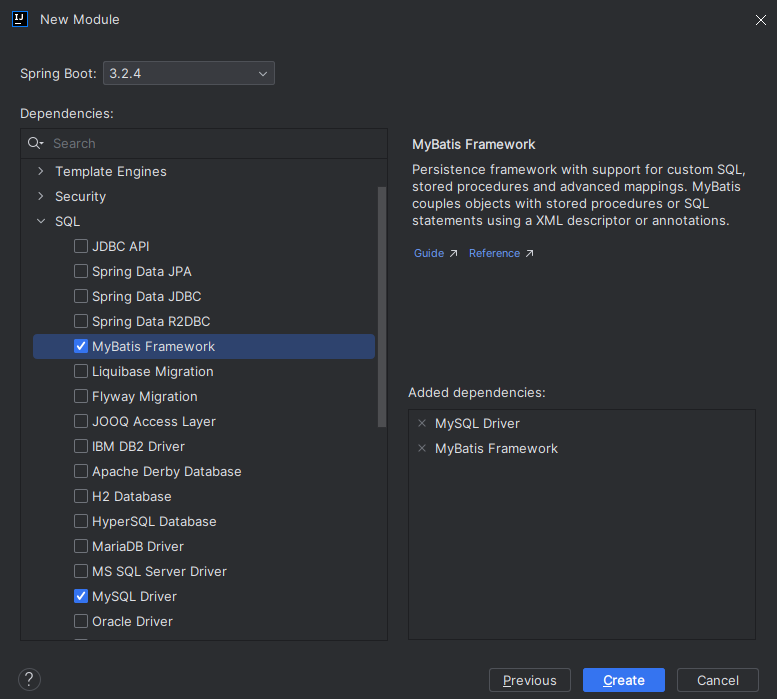
配置 application.yml 连接数据库
yml
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ssm_db
username: root
password: 123456
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource使用了 druid 连接池,需要在依赖中引入
xml
<!-- 添加 druid 连接池 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.2.6</version>
</dependency>写一个 User bean
java
package com.fan.domain;
public class User {
public int id;
public String name;
public int type;
public String description;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", type=" + type +
", description='" + description + '\'' +
'}';
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(int type) {
this.type = type;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public void setDescription(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
}写 UserDao
java
package com.fan.dao;
import com.fan.domain.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
@Mapper
public interface UserDao {
@Select("select * from user where name = #{name}")
public User getByName(String name);
}测试一下 getByName 方法
java
package com.fan;
import com.fan.dao.UserDao;
import com.fan.domain.User;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class SpringBoot06MybatisApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
User fan = userDao.getByName("fan");
System.out.println(fan);
}
}得到运行结果